What’s GST, CGST, SGST, IGST, Description of GST, CGST, SGST, IGST The present system of circular taxation has multifariousness of levies levied by the Centre and State. This has led to a complex and disagreeing principles in circular duty structure, adding to the multiple compliance and executive costs. There’s no uniformity in duty rates and structure across States. There’s slinging of levies due to‘ duty on duty’. There are too numerous restrictions on flawless credit available, i.e., credit of excise duty and service duty paid at the stage of manufacture isn’t available to the dealers while paying the State position deals duty or Handbasket, andvice-versa. Further, no credit of State levies paid in one State can be profited in other Countries. (CST). In this composition you may find complete details for all GST Acts like – What’s CGST, What id SGST, What’s IGST, What’s GST etc …
.
Goods and Service Tax, which subsumes a large number of Central and State levies into a single duty, is meant to alleviate the slinging effect of levies, give flawless credit and make way for a common request. Still, consummation of all the anteceding objects appears to be a Herculean task and requires the co-operation of all States.
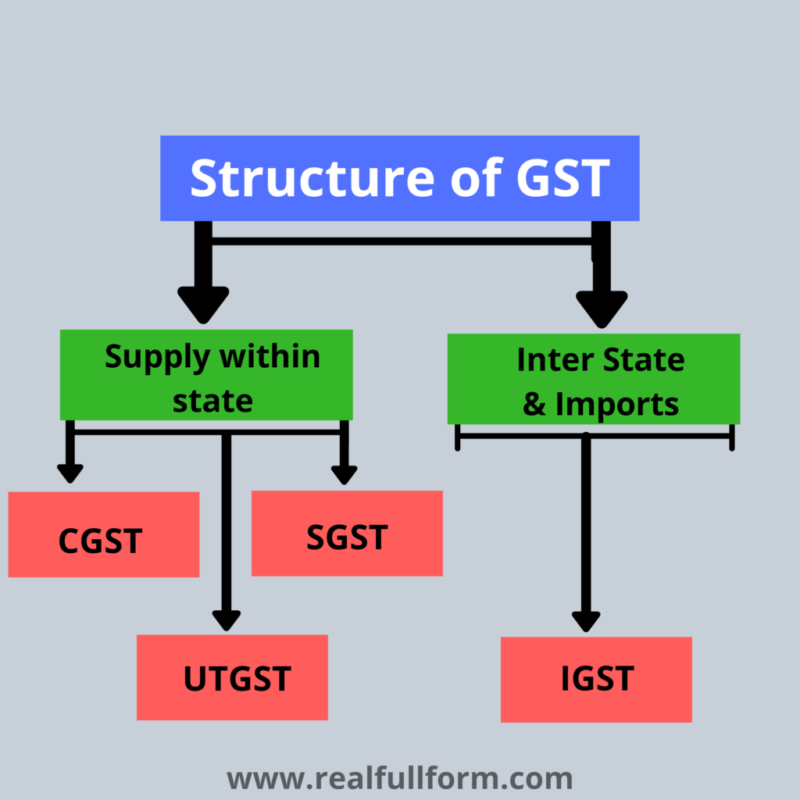
What is GST, CGST, SGST, IGST
What is GST (Goods and Service Tax)?
GST is a destination grounded duty and levied at a single point at the time of con sumption of goods or services by the ultimate consumer. GST is grounded on the principle of value added duty. GST law emphasizes on voluntary compliance and on accounts grounded reporting and covering system. It’s a comprehensive tax and envisages duty collection on both goods and services at the same rate Internationally, GST was first introduced in France and now further than 160 countries have introduced GST. Utmost of the countries, depending on their own socio-profitable conformation, have introduced Public position GST or Binary GST.
Description of Good and Service Tax (GST)
The term GST is defined in Composition 366 (12A) to mean “ any duty on force of goods or services or both except levies on force of the alcoholic liquor for mortal consumption In terms of Section 2 (52) of the CGST Bill “ Goods” means every kind of portable property other than plutocrat and securities but includes practicable claims, growing crops, lawn and other effects attached to or forming part of land which are agreed to be disassociated before force or under a contract of force In terms of Section 2 (102) of the CGST Bill “ Services” means anything other than goods, plutocrat and securities but includes exertion relating to the use of plutocrat or its conversion by cash or by any other mode, from one form, currency or denotation, to another form, currency or denotation for which a separate consideration is charged Therefore, all force of goods or services or both would attract CGST (to be levied by Centre) and SGST (to be levied by State) unless kept out of the horizon of GST.
Central Goods and Service Tax (CGST)
The Central GST (CGST) is anticipated to replace the being central excise duty and service duty. CGST would also cover trade deals The Indigenous Amendment Act, 2016 contains suitable vittles to enable Centre to duty deals. CGST would be administered by the Central Government. The CENVAT credit balance available under CENVAT Credit Rules with the manufacture or service provider, as on the date of transition into GST, could be carried forward. In respect of duty paid goods in stock as on the date of transition credit not profited in the history or not eligible at that point of time, available under GST could also be profited and used towards outlaying CGST (Central GST) liability. There could be a time bound transition for carry forward of credit profited previous to preface of GST. The protestation of closing stock as on the date of transition to claim credits, which weren’t before captured, would also be time bound.
State Goods and Service Tax (SGST)
State GST would replace State Handbasket, Entry duty, Octroi, Luxury duty, Entertainment duty etc. SGST would be levied on services as well. To enable taxing of services by the State, the Indigenous Amendment Act, 2016 contains suitable vittles. SGST is to be administered by the State Governments. SGST could be at a rate bit advanced than CGST as per press reports. The SGST outstanding could be set off from the SGST credit or the IGST credit available. The ending input Handbasket balance available under Handbasket Act would also be made available to the dealer, as on the date of transition into GST, and could be set off towards SGST (State GST) liability. Further it’s anticipated that the duty and duty paid on closing stock would also be available as credit, which may not have been claimed as set off in the Handbasket governance.
Inter State Goods and Service Tax (IGST)
IGST ( anticipated to be equal to CGST SGST) would be levied on all inventories of goods and/ or services in the course ofinter-state trade or commerce. IGST would be applicable to import of goods or services from outside country as well, which is indicated in the Indigenous Amendment Act, 2016. Further it’s anticipated that the duty and duty paid on closing stock would also be available as credit, which may not have been claimed as set-off.